
Drought has been a growing problem globally, with parts of the southwestern US being particularly affected. In fact, the region is currently experiencing a “megadrought” – the most severe drought in 1,200 years.
Colorado is part of this megadrought and, as a result, has experienced reduced snowpack, lowered lake and river levels, and a decline in the available groundwater. Add to that the overall dryness of the state and the fact that Colorado relies solely on precipitation for its water, and you have a recipe for disaster.
Overall, Colorado averages only 17 inches of precipitation annually. San Luis Valley is the driest region and only receives around seven inches of precipitation annually.
In short, the water in Colorado is highly precious. And since drought is set to continue being the norm for the foreseeable future, we must find ways to preserve its use and find more efficient methods for watering the crops and livestock in Colorado’s 38,900 farms and ranches.
Solar energy can be part of the solution. Through its use, we can apply better efficiency to agricultural water use and ensure we can ride out this drought and contribute to a more sustainable future.
In a Nutshell
- Solar-powered soil monitoring helps you understand soil moisture levels so you can optimize your watering system.
- Solar-powered irrigation systems give you more freedom and flexibility over watering your farm, which can help reduce wastage.
- Solar-powered drip irrigation is a precision-controlled watering system that maximizes water use, so you don’t need to consume as much of it.
- Floating solar panels can reduce water evaporation by over 60%.
- Solar panel water harvesting is a simple but effective way to collect rainwater from your solar panels.
- Solar hydro panels have the potential to revolutionize how we harvest water.
- Agrivoltaics significantly reduces soil water evaporation and retains soil moisture, reducing watering needs overall.
Solar-Powered Soil Monitoring

Soil monitoring is essential for many reasons. As a farmer, you constantly look for ways to maximize your crop yield while ensuring they are healthy and robust.
Using a monitor, you can understand the temperature, humidity, light conditions, soil moisture, and nutrition, giving you a rounded view of your crop’s environment and the ability to spot problem areas and rectify them.
With the use of solar energy, you can now apply soil monitoring to just about any area of the farm. Rather than relying on batteries, which have the habit of regularly running flat, a solar-powered monitor will run every day, giving you more consistent and reliable data.
How Does Solar-Powered Soil Monitoring Save Water?

Constant soil monitoring will tell you exactly how much moisture there is in the ground and whether it is sufficient to keep your crops happy.
By monitoring different areas of your farm, you can build a clear picture of which areas get dry quickly and which areas retain more moisture.
When you know this, you can adapt your watering system to deliver more water to the areas that require it most, and reduce it in the areas that don’t.
This helps you better manage and optimize water usage, resulting in a reduction of waste and over-watering.
Pros and Cons of Solar-Powered Soil Monitoring
Pros
The obvious pro is the data the monitoring system gives you. Additionally, monitoring systems are small – often with a built-in solar panel – and can be placed or moved anywhere you need them.
Cons
Unfortunately, monitoring systems need a way to send all that useful data to a computer or device. To do this, they need a WiFi connection or the use of a 3G/4G/5G network.
Since farms tend to be in remote areas, there often isn’t any kind of coverage for this. When you compare Colorado with the rest of the USA – especially the eastern states – for mobile network availability, you can see the state overall lacks coverage.
Solar-Powered Irrigation Systems

One of farming’s biggest challenges is ensuring crops are sufficiently watered. During drought, this becomes even more challenging to combat, particularly on farms that have large amounts of acreage to cover.
When precipitation is scarce, using irrigation is the favored way to ensure water gets to drops.
An irrigation system – depending on its type – can pull water from a nearby source, such as a canal, well, creek, or spring, and deliver it to the crops using a motorized pump and a pump controller.
Grid-connected irrigation systems have several serious drawbacks:
- First, you have to invest in the additional cabling required to power your pump(s). This is usually expensive and often limits you to areas that are situated near your electricity meter.
- Second, you are beholden to your utility provider’s tariffs. If you need to power your irrigation system daily, this can significantly add to your energy bills.
- Third, because of the required proximity to the electrical source, remote areas of the farm will be left without irrigation and require a different solution, such as running a generator (also very costly).
On the other hand, solar panels can be placed anywhere on the farm (provided there is sufficient sunlight). They also don’t need to be grid-connected, which gives you the flexibility to create an irrigation system that works for your farmland.
Not only does this give you a more efficient system, but it also brings the cost of running it down significantly because you’re not relying on your utility company (and its costly tariffs) to deliver the power.
How Do Solar-Powered Irrigation Systems Save Water?

The irrigation system itself isn’t going to do much to conserve water. However, the placement and flexibility of the solar panels allow you to gain precision control over the areas of the farm that receive the water.
Because you’re not limited to where you place your power source, it’s possible to attain a more even spread of watering and easily reach those remote areas. When your watering system works optimally, you will waste less water overall.
Furthermore, solar panels deliver power during daylight hours, which is precisely the time that crops dry out and require watering. Then, during the night – when crops don’t require water – the solar system shuts down and the irrigation system stops pumping.
This removes the ability – and the temptation – to keep irrigation systems running at night, which further reduces water consumption.
Pros and Cons of Solar-Powered Irrigation

Pros
The two biggest pros of solar-powered irrigation are that it vastly reduces your reliance on the grid and, in turn, vastly reduces your energy bills and it gives you the ability to deliver water to remote areas of your farmland. With careful use, it can also help conserve water or at least allocate it more efficiently.
Cons
On the flip side, when you’re not paying to power your irrigation system, it can be appealing to over-exploit water sources. So rather than conserving water, overusing it can have the opposite effect.
Consider this when designing your irrigation system and ensure that you are not drawing too much from a single source.
The other con is the increased cost of developing a solar-powered irrigation system. You need all the necessary solar equipment to run the system as well as any additional irrigation equipment to optimize its efficiency.
While this can all quickly add up, you have to consider the long-term savings gained in the reduction of your power bills, plus less crop spoilage thanks to your efficient watering system.
Solar-Powered Drip Irrigation

Following on from a standard irrigation system that typically sprays water onto a field, a drip irrigation system allows even more precision and control.
Using a network of tubing with emitters, it is laid among crops and allows water to be delivered directly to the plant’s roots – exactly where it needs to be – on a consistent basis.
This type of setup can also incorporate a feeding system, delivering liquid fertilizer when needed.
Like standard irrigation, a drip system needs electricity to power it either via the grid or a gas-powered generator. However, using solar panels removes this requirement and will enable your drop irrigation to run independently.
How Does Solar-Powered Drip Irrigation Save Water?

Drip irrigation can increase water efficiency by up to 90%. Since you’re delivering the water directly to the roots, it significantly reduces water runoff and wastage.
Because of the precision, you don’t need to use nearly as much water, which goes a long way toward conserving its use and sustainable farming practices.
Pros and Cons of Solar-Powered Drip Irrigation
Pros
Drip irrigation is a lot more efficient than standard irrigation, which can only achieve around 65% – 75% efficiency. Additionally, it helps prevent disease by reducing water contact with the crop’s leaves and fruit.
It’s also good for reducing weed growth as it keeps the rows between crops drier and it’s a particularly good strategy for crops on sloped ground where water runoff is more of an issue.
Cons
The additional equipment required for drip irrigation can be very costly, particularly if it’s required to cover a large area.
Even though you will save on your energy bills through the use of your solar panels, it’s worth noting that drip irrigation does require more maintenance than standard irrigation (when the tubes become blocked, etc.), which will result in increased costs.
Floating Solar Panels
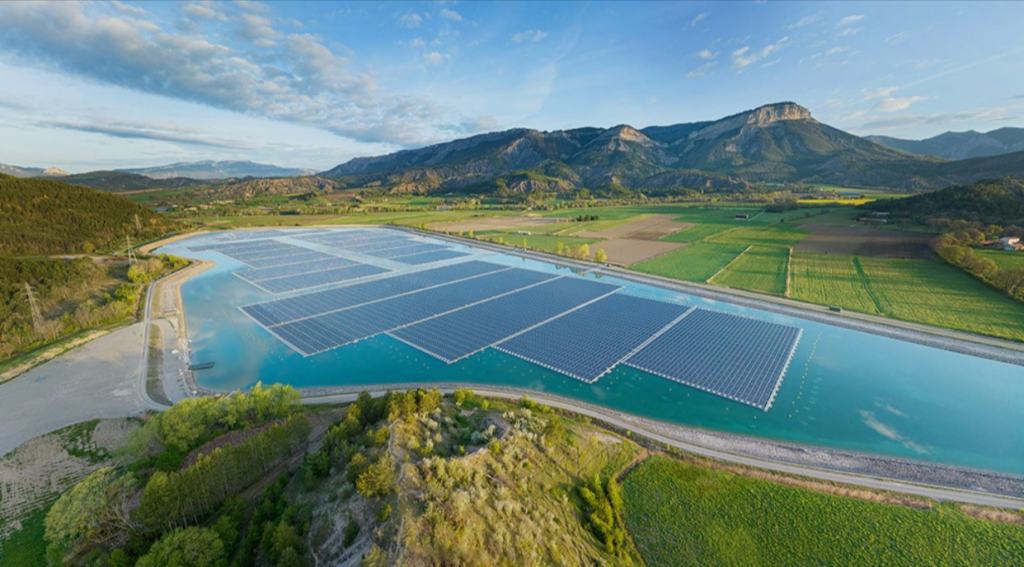

Also known as “floatovoltaics,” floating solar panels are installed so that they lay across a body of water. They are connected together in a grid-like fashion using a buoyant racking system and lay about three feet off the surface of the water. This allows the panels to move with the motion of the water but not get constantly submerged.
You will most commonly find floating solar panels on reservoirs, lakes, and other calm bodies of freshwater that are otherwise unused.
Floating solar panels are an interesting solution for powering irrigation systems that draw water from open bodies of water. Doing so increases water conservation efforts and ensures there is more available for crop watering.
How Do Floating Solar Panels Save Water?
Since the floating solar panels create a barrier between the sun and the water’s surface, they decrease the amount of water evaporation that occurs throughout the day. This can be substantial. One study in Brazil found that water evaporation was reduced by over 60% when floating solar panels were used.
This is why this setup is so advantageous for irrigation water sources. You get the power required to run the irrigation system and the panels conserve the water that is already there – it’s win-win!
Floating Solar Panels Pros and Cons
Pros
In addition to reducing water evaporation, floating solar panels don’t take up valuable land space that could be used for farming. The panels are also quite effective at preventing algae blooms from forming.
They are especially good for open bodies of water used for irrigation purposes or otherwise redundant water sources such as quarry lakes.
Cons
The main disadvantage of floating solar panels is their potential to interfere with local wildlife.
The panels reduce the amount of space for water birds and fowl to land, nest, and hunt for food. Furthermore, the panels restrict the amount of sunlight entering the water, which can negatively affect underwater flora and fauna.
Solar Panel Rainwater Harvesting

This is an interesting area that is starting to be explored more and more. Due to the positioning of solar panels, they offer the same advantages as a roof. When it rains, the water hits the surface of the panels and slides right off and onto the ground.
Unless you have an agrivoltaics setup (which we explore below) the rainwater falls onto ground that doesn’t require watering. In fact, it’s better not to water the ground as this encourages vegetation to grow and increases the maintenance required to keep it down.
Perhaps the most simplistic way to harvest the rainwater collected by solar panels is to install guttering which runs to a storage tank or to where it’s needed.
This is great for smaller water needs such as animal troughs and greenhouses. If you collect rainwater in storage tanks, this can build up for use during Colorado’s driest months.
Solar and Rainwater Harvesting: Recent Developments
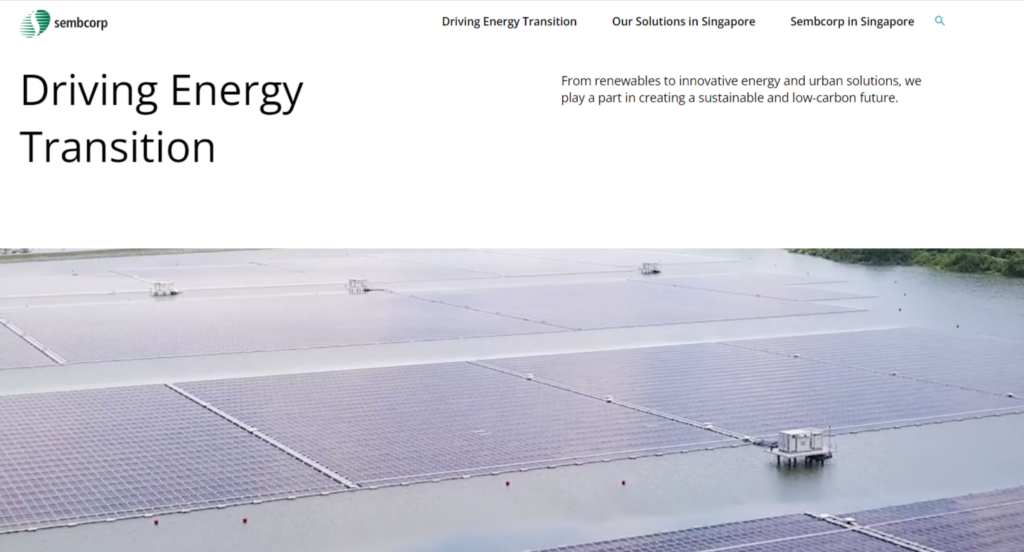
In other, more exciting developments, a solar farm with integrated water harvesting developed by Sembcorp has opened in Singapore. It has the capacity to collect more than 68 Olympic-size swimming pools worth of water annually, which will be used to clean and cool the panels for maximum efficiency.
A new technology that we’ll be watching with interest is the use of solar hydro panels. Like solar panels, hydro panels harvest the sun’s energy. This is used to power fans inside the panels that extract moisture from the air.
The air inside the panels switches the water vapor into liquid form which gets delivered to a plumbing or water storage system.
If this technology is successful, it has the potential to solve many of the USA’s drought problems. It has been developed by Arizona-based startup Source. It’s exciting stuff!
How Does Solar Rainwater Harvesting Save Water?
Harvesting the rainwater from your solar panels is a relatively inexpensive way to make use of the rainwater that would otherwise be lost. While it’s highly unlikely to address all of your water needs, it still allows you to preserve more of this precious resource and use it practically.
Solar hydro panels have the ability to generate water from thin air. If this venture is successful, it has the potential to significantly reduce the amount of water we take from the dwindling groundwater reserves.
Pros and Cons of Solar Rainwater Harvesting
Pros
Setting up a water collection system for your solar panels won’t require much of a financial outlay and gives you free access to water that would simply drain into the ground and be lost.
Cons
The amount of rainwater you collect – particularly in dry Colorado – will not be a huge amount. Additionally, you’re limited to collecting water and using it near where your solar panels are installed.
Agrivoltaics

Of all the ways in which solar technology can help with water conservation, agrivoltaics is probably the biggest and most promising.
Agrivoltaics is the practice of combining crop farming or animal grazing in the same space where the solar panels are installed. Typically, the solar panels are installed higher off the ground, allowing sufficient space for crops to thrive underneath.
This practice has multiple benefits. The panels provide much-needed shade during the hottest hours. This reduces heat stress and UV damage, resulting in better yields.
Additionally, the microclimate generated beneath the panels allows biodiversity to thrive positively. Better still, the cooler day temperature and warmer night temperature increase soil moisture and reduce soil erosion, water runoff, and evaporation. In one scientific study, water evaporation under an agrivoltaic system was reduced by 21%.
Another two-year study on a six-acre agrivoltaic farm in Oregon recorded an incredible 328% higher water efficiency rate for the soil underneath the solar panels compared with non-covered soil.
Agrivoltaics has been widely used in Europe and parts of Asia for a couple of decades. The US has been slow to catch up, but as water becomes scarcer, this farming practice is starting to get increasingly adopted. If you want a great Colorado-based example of agrivoltaics, be sure to check out Jack’s Solar Garden in Longmont.
How Does Agrivoltaics Save Water?

Since agrivoltaics does such a great job of retaining soil moisture and reducing water evaporation, your crops will need watering a lot less.
Additionally, since the panels keep the day temperatures cooler, your crops will get thirsty less often too.
Agrivoltaics Pros and Cons
Pros
Agrivoltaics has the potential for an incredible number of benefits. The space beneath the panels provides the ideal growing environment for better, healthier crop yields resulting in more profit for your farm while reducing production and maintenance costs.
Furthermore, agrivoltaics makes double use of a single space. You don’t have to choose between using the space for solar energy or farming – now you can do both!
Cons
An agrivoltaics setup requires more costly equipment, mainly because the panels have to be raised higher off the ground. This is especially true if you want enough space to drive farm machinery underneath.
It could also mean that you have to overhaul your entire farm setup in order to switch to agrivoltaics farming. Not all crops are suitable for agrivoltaics so what you plant underneath must be shade-tolerant to a degree.
Final Thoughts

Solar energy has the potential to achieve so much more than free and sustainable electricity. By applying it to water management systems or adopting agrivoltaics, you can unlock solar’s other benefits and significantly reduce the amount of water you consume.
At 8760 Solar, we’re in constant awe of the advantages solar energy can bring to our customers. We understand our farmers in Colorado face growing challenges when it comes to available resources and the affordability of obtaining them and we’re confident that solar is part of the solution.
Why choose 8760 Solar?
- We specialize in providing solar to Colorado’s farms and agricultural businesses
- We provide a full analysis of your farm to determine the best solar setup for your needs
- We’ll help you take full advantage of all available tax credits and incentives
- All our prices and processes are fully transparent and fair
- We’re reliable and friendly, and we’re here to answer all of your questions!
Text “READY” to 719 470-0254 or contact us via email: sales@8760solar.com and we’ll be in touch with you right away.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can Solar Energy Help Save Water?
Solar energy can be used to power monitoring and irrigation systems, which allow more precise and effective watering practices. Additionally, agrivoltaics reduces watering requirements. And rain harvested from the solar panels themselves provides an additional source of water.
How Does Agrivoltaics Help Water Conservation?
Using an agrivoltaics setup creates a cooler daytime temperature and a warmer nighttime temperature beneath the panels. This unique microclimate significantly reduces water evaporation and increases soil moisture.
Because of this, less crop watering is required for anything grown beneath the solar panels.
How Can I Harvest Rainwater From My Solar Panels?
Rainwater can easily be harvested from your solar panels by installing guttering along the bottom of the panels. You can then connect the gutting to a water storage tank or reservoir for later use.
What Are Solar Hydro Panels?
Solar hydro panels look similar to solar panels but they work very differently. They use the sun’s energy to power fans contained within the panels. The fans draw in moisture vapor from the air, which is then transformed into liquid form. The harvested water is then delivered into the plumbing system or stored in a tank for later use.
Can I Retrofit an Irrigation System to Have Solar Energy?
Yes! You can retrofit an irrigation system to run off solar energy instead of the grid. Your solar developer will be able to talk to you about off-grid solar systems and what would be required to power your irrigation needs.
